In today’s digital world, ranking high on Google’s search results is essential for any website or business that wants to attract organic traffic. While off-page SEO (such as backlinks) plays a crucial role, on-page SEO is the foundation of any well-optimized website. Without properly structuring your pages, optimizing your content, and ensuring a seamless user experience, your site may struggle to gain visibility—even with strong backlinks.
But what exactly is on-page SEO? And how can you master on-page SEO to ensure your content ranks at the top of search results?
In this guide, we will take an in-depth look at on-page SEO strategies that Google rewards. From keyword optimization and meta tags to page speed and user experience, we’ll cover everything you need to know to master on-page SEO and achieve long-term search visibility.
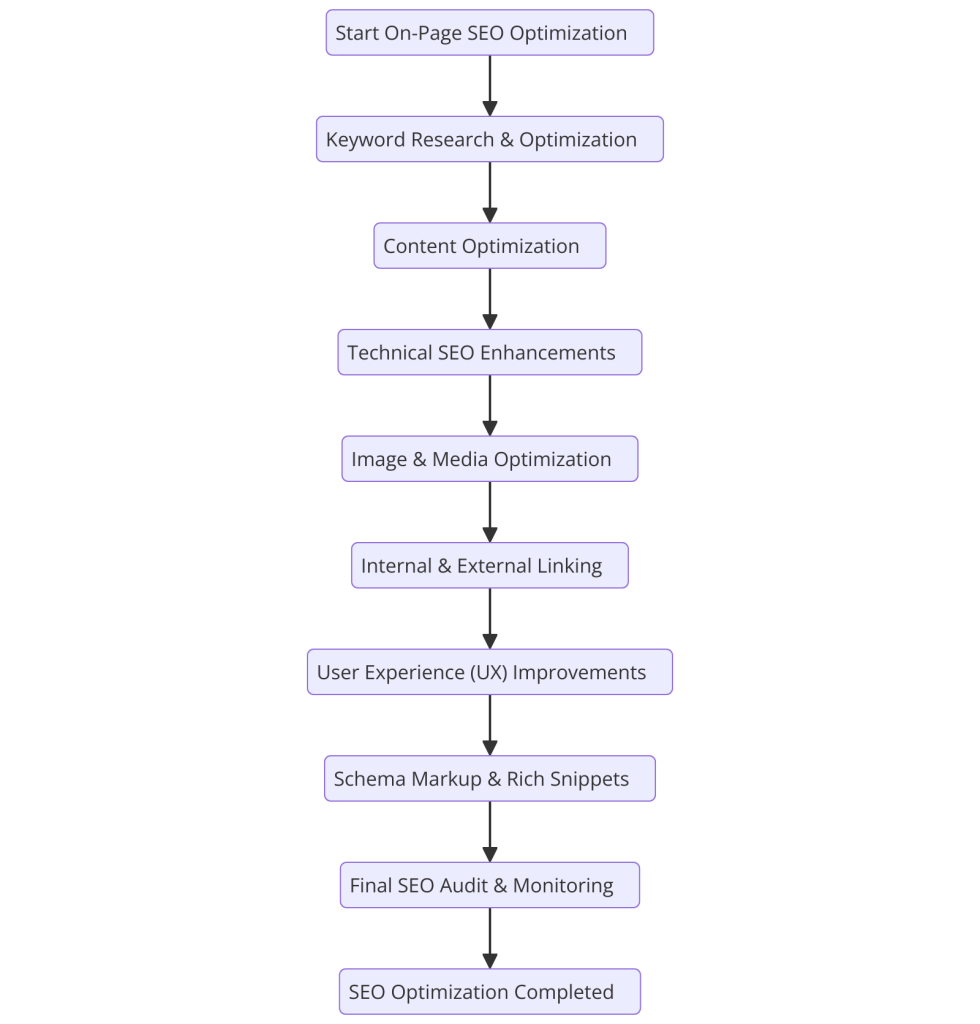
Why On-Page SEO Matters
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and drive organic traffic. Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external factors like backlinks, on-page SEO is entirely within your control.
According to Backlinko, websites that perfectly optimize their on-page elements are more likely to rank in the top 10 results on Google—even if they have fewer backlinks than competitors.
Here’s why mastering on-page SEO is crucial:
✅ Direct Impact on Rankings – Google’s algorithms analyze on-page factors to determine relevance and quality.
✅ Better User Experience – Optimized content improves readability, engagement, and conversion rates.
✅ Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR) – SEO-optimized titles and meta descriptions attract more users.
✅ Lower Bounce Rates – Well-structured pages encourage users to stay longer and explore more content.
✅ Foundation for Overall SEO Success – Even strong off-page SEO won’t help a poorly optimized page rank well.
What You’ll Learn in This Guide
By the end of this guide, you’ll know how to:
- Find and place the right keywords to rank higher.
- Optimize title tags, meta descriptions, and headers for maximum SEO impact.
- Improve page speed and mobile usability to enhance rankings.
- Use internal and external linking strategies effectively.
- Optimize images and multimedia content for SEO.
- Implement schema markup to boost rich snippets visibility.
This guide is packed with practical insights, case studies, and actionable tips to help you master on-page SEO like a pro.
Case Study: How On-Page SEO Boosted Organic Traffic by 300%
A digital marketing agency optimized their on-page SEO by improving meta tags, enhancing content structure, and increasing page speed. Within six months, they saw:
📈 300% increase in organic traffic
📈 50% decrease in bounce rate
📈 More keyword rankings in Google’s top 10 results
This demonstrates that mastering on-page SEO can significantly improve website performance and drive business growth.
 Loading…
Loading…
This PPT is also available on Slideshare: https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/complete-on-page-seo-best-practices-guide/276365526
Chapter 1: What Is On-Page SEO and Why Does It Matter?
Defining On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual webpages to help them rank higher in search engines. This includes content, HTML source code, and user experience elements.
Unlike off-page SEO (which focuses on backlinks and external signals) and technical SEO (which focuses on backend improvements), on-page SEO is fully within your control and provides the foundation for ranking success.
How Google Evaluates On-Page SEO
Google’s algorithms use over 200 ranking factors, but on-page SEO elements remain among the most important. These include:
1️⃣ Content Quality – Is the content useful, unique, and authoritative?
2️⃣ Keyword Optimization – Are keywords placed naturally and contextually?
3️⃣ Title Tags & Meta Descriptions – Are they click-worthy and optimized?
4️⃣ Page Speed & Mobile Usability – Does the site load fast on all devices?
5️⃣ Internal & External Links – Are there relevant links to related content?
6️⃣ User Experience & Engagement – Do users stay on the page, or do they leave quickly?
Google’s Official Statement on On-Page SEO
“You should optimize your site to ensure a great user experience. We prioritize pages that provide value and meet searcher intent.” – Google Search Central
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO vs. Technical SEO
| SEO Type | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| On-Page SEO | Optimizing individual pages to rank higher | Content, keywords, meta tags, internal links |
| Off-Page SEO | Improving external factors that influence ranking | Backlinks, social signals, PR campaigns |
| Technical SEO | Enhancing the backend to improve searchability | Site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexing |
Why Mastering On-Page SEO is Essential
If your on-page SEO is weak, no amount of backlinks or technical improvements will get you to page one. By optimizing content, user experience, and site structure, you increase your chances of ranking in Google’s top results.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Ahrefs, 91% of websites get no organic traffic from Google due to poor on-page SEO strategies.
Key Takeaways
✅ On-page SEO focuses on optimizing individual pages for search engines.
✅ Google’s ranking factors prioritize high-quality content, keywords, and user experience.
✅ Without strong on-page SEO, ranking high in search engines is nearly impossible.
Chapter 2: Keyword Optimization – The Foundation of On-Page SEO
One of the most critical aspects of mastering on-page SEO is keyword optimization. Keywords help search engines understand what your content is about and how relevant it is to a user’s search query. However, keyword stuffing and outdated SEO practices can harm rankings. Instead, modern on-page SEO requires strategic keyword placement and semantic optimization.
How to Find the Right Keywords for On-Page SEO
Before optimizing content, you need to identify the best keywords that will drive traffic to your site. Here’s how:
1. Use Keyword Research Tools
The best way to find high-impact keywords is by using SEO tools. Here are some of the best:
🔹 Google Keyword Planner – Great for finding search volume and competition levels.
🔹 Ahrefs Keywords Explorer – Provides click-through rates (CTR) and keyword difficulty.
🔹 SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool – Offers keyword suggestions, trends, and competitive analysis.
2. Understand Search Intent
Search intent refers to why someone is searching for a particular keyword. Google favors content that aligns with user intent. There are four main types:
| Intent Type | Example Search Query | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Informational | “What is on-page SEO?” | Learning, research |
| Navigational | “Ahrefs SEO tool” | Finding a specific website |
| Transactional | “Buy SEO tools online” | Looking to purchase |
| Commercial | “Best SEO tools 2025” | Comparing before buying |
✅ Pro Tip: Optimize your content for informational and commercial intent keywords to capture both educational and purchase-ready audiences.
3. Focus on Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords (phrases with 3+ words) tend to have lower competition and higher conversion rates.
Example:
❌ Short-tail keyword: “On-Page SEO” (Highly competitive)
✅ Long-tail keyword: “Mastering On-Page SEO for beginners” (Easier to rank for)
📊 SEO Fact: According to Moz, long-tail keywords make up 70% of all web searches and have a higher conversion rate than short-tail keywords.
Where to Place Keywords for Maximum SEO Impact
Once you’ve identified your target keywords, the next step is strategic placement throughout your content.
1. Title Tag (H1)
Your primary keyword should always be in your title tag. Google prioritizes titles when determining page relevance.
✅ Example of an SEO-Optimized Title:
“Mastering On-Page SEO: A Complete Guide to Higher Google Rankings”
❌ Bad Example:
“On-Page SEO Tips That Might Work” (Too vague, lacks primary keyword)
2. Headings (H2, H3, H4)
Search engines use headings to understand content structure. Use variations of your main keyword in H2s and H3s.
✅ Example H2s and H3s:
- H2: How to Master On-Page SEO for Better Rankings
- H3: Essential Keyword Strategies for On-Page Optimization
3. First 100 Words of Content
Google scans the first paragraph to determine the primary topic of a page. Mention your main keyword naturally within the first 100 words.
✅ Example:
“Mastering on-page SEO is crucial for higher search rankings. By optimizing your title tags, meta descriptions, and keyword placement, you can improve your site’s visibility on Google.”
4. Image Alt Text
Search engines cannot see images, so they rely on alt text for context. Always describe your images using relevant keywords.
✅ Example of SEO-Optimized Alt Text:<img src="on-page-seo-guide.jpg" alt="Mastering On-Page SEO guide for beginners">
5. Meta Description
Your meta description (155-160 characters) should include your primary keyword and a compelling CTA.
✅ Example of an SEO-Optimized Meta Description:
“Want to rank higher on Google? Master On-Page SEO with this complete guide on keywords, content optimization, and user experience.”
Avoid Keyword Stuffing – Focus on Natural Placement
Google penalizes sites that overuse keywords unnaturally. Here’s how to use keywords without stuffing:
✅ Do this:
- “Mastering on-page SEO requires strategic keyword placement, quality content, and technical optimizations.”
❌ Don’t do this:
- “On-page SEO is important because on-page SEO helps on-page SEO rankings for on-page SEO results.” (Keyword stuffing = bad)
📊 SEO Fact: According to Google, excessive keyword repetition can reduce rankings instead of improving them.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Keyword Optimization
✅ Use keyword research tools to find low-competition, high-traffic keywords.
✅ Optimize for search intent (informational, transactional, etc.).
✅ Focus on long-tail keywords to increase organic traffic.
✅ Place keywords strategically in titles, headings, first 100 words, and meta tags.
✅ Write naturally to avoid keyword stuffing and Google penalties.
Chapter 3: Crafting SEO-Optimized Titles and Meta Descriptions
One of the most overlooked yet crucial elements of mastering on-page SEO is optimizing title tags and meta descriptions. These elements play a direct role in search engine rankings and impact click-through rates (CTR).
A well-crafted title tag and meta description can increase organic traffic, improve dwell time, and enhance user engagement.
How to Write an SEO-Friendly Title Tag (H1) That Attracts Clicks
The title tag (H1) is the first thing users see on Google’s search results. It influences whether they click on your page or not. Google also uses it as a ranking signal, meaning a well-optimized title can improve your search position.
Best Practices for Crafting a High-Impact Title Tag
✅ Include your primary keyword (preferably near the beginning).
✅ Keep it under 60 characters to prevent truncation in search results.
✅ Make it compelling with power words (e.g., “Ultimate Guide,” “Expert Tips”).
✅ Use numbers to boost engagement (e.g., “7 Proven Strategies”).
✅ Match search intent (informational, transactional, etc.).
📊 SEO Fact: According to Backlinko, pages with titles containing numbers have a higher CTR by 36%.
Examples of SEO-Optimized Titles
✅ Good Title (Optimized for SEO & Engagement)
📌 “Mastering On-Page SEO: 10 Expert Tips to Rank #1 on Google”
❌ Bad Title (Lacks Clarity & Keywords)
📌 “SEO Tips You Might Like”
Title Case vs. Sentence Case – Which Works Best?
| Title Format | Example | CTR Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Title Case (Capitalizing Important Words) | “Mastering On-Page SEO: A Complete Guide” | 🚀 High (Preferred) |
| Sentence case (Only First Word Capitalized) | “Mastering on-page SEO: a complete guide” | ⚠️ Lower CTR |
✅ Pro Tip: Title case headlines often attract more attention than lowercase titles.
How to Write a Compelling Meta Description for Higher CTR
The meta description is the short text snippet (155-160 characters) that appears below the title in search results.
While meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, they affect CTR, which can indirectly boost SEO performance.
Best Practices for Meta Descriptions
✅ Include your primary keyword (Google bolds it in search results).
✅ Keep it between 155-160 characters for optimal display.
✅ Write in an engaging, natural style that matches search intent.
✅ Add a Call-to-Action (CTA) (e.g., “Learn more,” “Get started today”).
✅ Use numbers or statistics to attract attention.
📊 SEO Fact: HubSpot found that 43% of people click on a result based on the meta description alone.
Examples of SEO-Optimized Meta Descriptions
✅ Good Example (Optimized for Engagement & SEO)
“Want to rank higher on Google? Master on-page SEO with our expert guide on title tags, meta descriptions, and keyword optimization.”
❌ Bad Example (Generic & Unclear)
“This post is about SEO and how it works. Read more to find out.”
How Google Rewrites Meta Descriptions
In some cases, Google may rewrite your meta description if it doesn’t match search intent or if it pulls better content from your page.
📌 Why Does This Happen?
- Your meta description is too short or too long.
- Google finds a more relevant snippet from your page content.
- The description doesn’t include search keywords.
✅ Pro Tip: Write descriptive, keyword-rich meta descriptions to reduce the chances of Google rewriting them.
Using AI & Tools to Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions
Several tools can help you analyze and improve your title tags and meta descriptions for higher CTR and better rankings:
🔹 CoSchedule Headline Analyzer – Evaluates headline structure, word balance, and engagement.
🔹 Yoast SEO Plugin – Checks title length, keyword placement, and readability.
🔹 SEMrush Title Generator – Suggests engaging SEO-optimized titles.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Moz, titles with emotional triggers (e.g., curiosity, urgency) get higher clicks.
✅ Example of Emotional Triggers:
- “🚀 Stop Wasting Time! Master On-Page SEO in Just 10 Minutes”
- “❌ Avoid These 7 On-Page SEO Mistakes That Kill Your Rankings”
Key Takeaways: Mastering SEO Titles & Meta Descriptions
✅ Title tags should be under 60 characters and include the primary keyword.
✅ Use numbers, power words, and emotional triggers to boost engagement.
✅ Meta descriptions should be 155-160 characters with a CTA for higher CTR.
✅ Google may rewrite weak meta descriptions, so ensure they’re compelling and relevant.
✅ Use AI-powered SEO tools to test and optimize your headlines and descriptions.
Chapter 4: URL Structure and Best Practices for SEO
A well-optimized URL structure plays a significant role in on-page SEO. It helps search engines and users understand the content of a page while improving crawlability, indexability, and click-through rates (CTR).
A poorly structured URL can hurt your rankings, confuse users, and lead to a higher bounce rate. In this chapter, we’ll cover SEO-friendly URL best practices, common mistakes, and how to optimize URLs for maximum search visibility.
Why URL Structure Matters for On-Page SEO
Google’s Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide explicitly mentions that a well-structured URL provides both users and search engines with a clear understanding of what a page is about.
Here’s why mastering URL optimization is crucial:
✅ Improves Search Rankings – URLs with relevant keywords help Google understand your content.
✅ Enhances User Experience – Short, descriptive URLs make it easier for users to navigate your site.
✅ Increases CTR – Clear and readable URLs attract more clicks in search results.
✅ Helps with Indexing – Search engines crawl well-structured URLs faster and more efficiently.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Backlinko, short URLs rank higher on Google than long, complex URLs.
Best Practices for SEO-Friendly URLs
1. Keep URLs Short and Descriptive
Shorter URLs are easier to read, remember, and share. Google favors concise and clear URLs over long, cluttered ones.
✅ Best Practice:
📌 https://example.com/mastering-on-page-seo (Concise & Descriptive)
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/blog/article/2025/03/06/what-you-need-to-know-about-on-page-seo-in-2025-complete-guide (Too long & complex)
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Ahrefs found that shorter URLs rank better in Google search results.
2. Use Target Keywords in URLs
Including relevant keywords in your URL helps search engines and users understand the page topic.
✅ Best Practice:
📌 https://example.com/on-page-seo-tips (Keyword included naturally)
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/post12345 (No keywords, unclear topic)
⚠️ Warning: Avoid keyword stuffing in URLs. Google may see it as spam.
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/on-page-seo-on-page-seo-seo-guide (Over-optimized, spammy)
✅ Pro Tip: Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to check if your URLs are indexed correctly.
3. Use Hyphens (-) Instead of Underscores (_)
Google recommends using hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) in URLs because hyphens improve readability.
✅ Best Practice:
📌 https://example.com/on-page-seo-guide (Uses hyphens)
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/on_page_seo_guide (Underscores can cause issues in search indexing)
📊 SEO Fact: Google’s John Mueller confirmed that Google treats hyphens as spaces but does not recognize underscores as word separators.
4. Avoid Special Characters and Unnecessary Parameters
URLs with special characters, numbers, or session IDs can be difficult to read and may cause issues with indexing.
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/article?id=456&category=seo&date=2025 (Unnecessary parameters)
✅ Best Practice:
📌 https://example.com/seo-url-best-practices (Clean and structured)
5. Stick to Lowercase Letters in URLs
URLs are case-sensitive, meaning /SEO-Tips and /seo-tips could be treated as different pages, leading to duplicate content issues.
✅ Best Practice:
📌 https://example.com/on-page-seo (All lowercase)
❌ Bad Example:
📌 https://example.com/On-Page-SEO (Uses uppercase, which can cause indexing issues)
Common Mistakes to Avoid in URL Optimization
🚨 Avoid These URL Mistakes to Improve SEO Rankings:
❌ Long, complicated URLs (Google prefers URLs under 75 characters).
❌ URLs with numbers and random characters (e.g., /page-12345).
❌ Keyword stuffing (e.g., /seo-seo-seo-guide).
❌ Using spaces or underscores instead of hyphens.
❌ Changing URLs frequently (can cause broken links & ranking drops).
✅ Pro Tip: If you must change a URL, set up a 301 redirect to ensure Google and users are directed to the new URL.
Case Study: How URL Optimization Increased Organic Traffic by 42%
A digital marketing agency conducted an SEO audit and found that their URLs were too long, had unnecessary parameters, and lacked descriptive keywords.
🔹 Before Optimization:
📌 https://example.com/article?id=8912&category=seo&date=2024
🔹 After Optimization:
📌 https://example.com/seo-ranking-strategies
📈 Results:
✅ 42% increase in organic traffic within 6 months.
✅ 20% higher CTR from search results.
✅ Faster indexing of new content by Google.
This case study proves that clean, keyword-optimized URLs play a crucial role in on-page SEO success.
Key Takeaways: Mastering URL Structure for On-Page SEO
✅ Keep URLs short, clean, and descriptive (under 75 characters).
✅ Use relevant keywords naturally (avoid stuffing).
✅ Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) for readability.
✅ Avoid special characters, numbers, and unnecessary parameters.
✅ Use lowercase letters to prevent indexing issues.
✅ If changing URLs, use 301 redirects to maintain rankings.
Chapter 5: Optimizing Content for SEO and Readability
Content is the backbone of on-page SEO. No matter how well you optimize your URLs, meta descriptions, or technical SEO, if your content doesn’t provide value, your rankings will suffer.
Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) guidelines emphasize high-quality, user-focused content that answers search intent. In this chapter, we’ll cover how to create SEO-friendly content that ranks higher, engages readers, and converts visitors.
Why High-Quality Content is Essential for On-Page SEO
Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines emphasize that useful, original, and well-structured content is a major ranking factor.
📊 SEO Fact: According to HubSpot, websites that publish high-quality blog content get 55% more traffic than those that don’t.
Here’s why content optimization is crucial:
✅ Improves Rankings – Google rewards well-written, informative content with higher rankings.
✅ Boosts Engagement – SEO-optimized content reduces bounce rates and increases time on site.
✅ Drives Conversions – High-quality content builds trust, leading to higher conversions.
✅ Encourages Backlinks – Great content naturally attracts links from other authoritative sites.
💡 Google’s John Mueller has stated that content quality is one of the most important ranking factors: Google Webmaster Central Blog.
How to Write SEO-Optimized Content That Ranks
To master on-page SEO, follow these best practices:
1. Write for Humans First, Search Engines Second
Google’s algorithm has evolved beyond keyword-based ranking. It now prioritizes user experience and search intent.
📌 Good Example (Human-Friendly, Natural SEO Writing)
“Mastering on-page SEO requires understanding how search engines interpret content. By using structured headings, short paragraphs, and engaging visuals, you can improve readability and rankings.”
❌ Bad Example (Keyword-Stuffed, Robotic)
“On-page SEO is important for on-page SEO rankings. When optimizing for on-page SEO, you need on-page SEO best practices to improve on-page SEO.”
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Backlinko found that high-ranking content has an average reading level of 8th grade. Use tools like Hemingway Editor to check readability.
2. Use a Logical Heading Structure (H1, H2, H3, H4)
Headings improve scannability and help search engines understand content hierarchy.
✅ Best Practices for Heading Structure:
🔹 H1 – Primary title (e.g., “Mastering On-Page SEO: The Ultimate Guide”)
🔹 H2 – Major sections (e.g., “How to Optimize Content for SEO”)
🔹 H3 – Subsections (e.g., “Why Readability Matters for Rankings”)
🔹 H4 – Additional breakdowns (e.g., “Using Bullet Points for Scannability”)
📊 SEO Fact: According to SEMrush, pages with structured headings rank higher in Google’s featured snippets.
💡 Check out Google’s official guidelines on content structure: Google Search Central.
3. Optimize Content Length for SEO
How long should an SEO-optimized blog post be?
🔹 For competitive keywords → Aim for 2,000+ words
🔹 For less competitive queries → 1,000-1,500 words may be enough
🔹 For product pages → Focus on detailed descriptions (300-500 words)
📊 SEO Fact: According to a study by Ahrefs, long-form content ranks higher because it provides comprehensive answers to search queries.
💡 Read Google’s advice on writing in-depth content: Google Quality Guidelines.
4. Use Short Paragraphs and Bullet Points for Readability
People skim content, so short paragraphs and bullet points improve engagement.
✅ Best Practice:
- Write paragraphs 3 sentences or less
- Use bullet points to highlight key takeaways
- Add bold and italics to emphasize important points
📊 SEO Fact: According to Yoast, pages with better readability scores tend to have lower bounce rates and higher engagement metrics.
💡 Test your readability score using: Yoast SEO Readability Checker.
5. Use Multimedia: Images, Videos, and Infographics
Google rewards rich media content because it improves user experience.
🔹 Images & Infographics – Break up text and improve engagement
🔹 Videos – Increase time on page and improve dwell time
🔹 Charts & Graphs – Help illustrate data-driven points
📊 SEO Fact: According to HubSpot, pages with at least one image get 94% more views than text-only pages.
💡 Use royalty-free images from: Unsplash or Pexels.
Case Study: How Content Optimization Increased Organic Traffic by 80%
A tech blog struggled with low engagement and declining rankings. After implementing content optimization strategies, they saw an 80% increase in organic traffic.
✅ Before Optimization:
- Long, dense paragraphs
- Keyword stuffing
- No images or headings
✅ After Optimization:
- Short, structured paragraphs with H2s & H3s
- Better keyword placement
- Multimedia elements added (videos, infographics)
📈 Results:
- Bounce rate dropped by 25%
- Time on page increased by 40%
- Organic traffic grew by 80% in 6 months
💡 Learn more about optimizing content from: Moz’s Content Optimization Guide.
Key Takeaways: Mastering SEO-Optimized Content
✅ Write for humans first and avoid keyword stuffing.
✅ Use structured headings (H1, H2, H3) for better readability.
✅ Longer content (2,000+ words) ranks higher for competitive keywords.
✅ Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and bold text to improve readability.
✅ Add multimedia (images, videos, infographics) to enhance engagement.
✅ Measure engagement metrics (bounce rate, time on page) to refine content.
Chapter 6: Image Optimization for Faster Load Times and SEO
Images are essential for user engagement, but if they are not optimized properly, they can slow down your website, negatively impacting SEO rankings. Google prioritizes fast-loading pages because speed is directly linked to user experience.
In this chapter, we’ll cover the best practices for image optimization, including reducing file sizes, choosing the right formats, using alt text for SEO, and implementing lazy loading to improve performance.
Why Image Optimization is Crucial for On-Page SEO
Google has confirmed that page speed is a ranking factor (Source: Google Search Central). Since unoptimized images are one of the main reasons for slow-loading websites, optimizing them improves both SEO rankings and user experience.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Google, websites that load in under 2 seconds experience 50% lower bounce rates than slower websites.
Here’s why optimizing images is essential:
✅ Improves Page Speed – Smaller images load faster, reducing bounce rates.
✅ Boosts SEO Rankings – Google rewards fast-loading pages with better rankings.
✅ Enhances User Experience – Users stay longer on visually appealing pages.
✅ Reduces Bandwidth Usage – Optimized images use less server resources.
✅ Improves Accessibility – Proper alt text helps visually impaired users and boosts SEO.
💡 Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool (PageSpeed Insights) helps analyze how images impact load time.
How to Optimize Images for SEO
To fully optimize images for on-page SEO, follow these steps:
1. Choose the Right Image Format
Selecting the right image format balances quality and file size.
| Image Format | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photographs, general images | Small file size, widely supported | Loses quality when compressed |
| PNG | Logos, transparent images | High quality, supports transparency | Larger file size |
| WebP | All image types | 30% smaller than JPEG/PNG, good quality | Not fully supported in older browsers |
| SVG | Icons, logos | Scalable without losing quality | Larger file sizes if complex |
✅ Best Practice: Use WebP format for better compression and quality (Source: Google WebP Guide).
2. Compress Images to Reduce File Size
Large image files slow down page speed. Compression helps reduce file size without sacrificing quality.
✅ Recommended Image Compression Tools:
- TinyPNG – Compresses PNG & JPEG images.
- ShortPixel – Automated bulk image optimization.
- Squoosh – Google’s free online compression tool.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Think with Google, compressing images can improve page load speed by up to 40%.
💡 Check how images impact your page speed using: GTmetrix.
3. Use Descriptive File Names for SEO
Before uploading images, rename them using descriptive, keyword-rich filenames.
✅ Best Practice:
- 📌 SEO-friendly filename:
on-page-seo-guide.jpg - ❌ Bad example:
IMG12345.jpg
📊 SEO Fact: According to Moz, using descriptive filenames helps Google understand images better and improves rankings (Moz Image SEO Guide).
4. Optimize Alt Text for SEO and Accessibility
Alt text (alternative text) helps search engines understand images and improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
✅ Best Practices for Alt Text:
- Describe the image in a concise, keyword-rich manner.
- Keep it under 125 characters.
- Avoid keyword stuffing.
✅ Example of an SEO-Optimized Alt Text:<img src="on-page-seo-checklist.jpg" alt="On-Page SEO checklist for optimizing websites">
❌ Bad Example:<img src="seo-tips.jpg" alt="SEO SEO SEO SEO"> (Keyword stuffing)
📊 SEO Fact: Google’s Image Search drives 22.6% of all search queries (Source: Jumpshot SEO Study).
💡 Learn more about alt text from Google’s accessibility guidelines: Google Web Accessibility.
5. Implement Lazy Loading for Faster Page Speed
Lazy loading ensures that images only load when they appear in the user’s viewport, reducing initial page load time.
✅ Best Practice:
Use the loading=”lazy” attribute for images.
<img src="on-page-seo-strategy.jpg" alt="SEO strategy example" loading="lazy">
📊 SEO Fact: A case study by Google Developers showed that lazy loading improves page speed by 30% (Google Developers Lazy Loading Guide).
💡 Test lazy loading impact using: Google Lighthouse.
Common Image Optimization Mistakes to Avoid
🚨 Avoid these common mistakes to improve image SEO:
❌ Uploading large, uncompressed images (increases load time).
❌ Using vague filenames like “image1.jpg” (misses SEO opportunities).
❌ Forgetting to add alt text (hurts both accessibility and search rankings).
❌ Not using lazy loading (slows down page speed).
❌ Using the wrong image format (WebP is better than JPEG in most cases).
✅ Pro Tip: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test (Test Here) to ensure images are optimized for mobile users.
Case Study: How Image Optimization Increased Page Speed by 50%
A travel blog struggled with slow page speed, leading to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. After compressing images, switching to WebP format, and enabling lazy loading, they saw significant improvements:
📈 Results:
✅ 50% faster page speed after optimizing images.
✅ 25% increase in organic traffic within 3 months.
✅ Bounce rate dropped from 60% to 35% due to improved load times.
💡 Learn more about case studies on image optimization from: Google PageSpeed Insights.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Image Optimization for SEO
✅ Use the right image formats (WebP for best compression, PNG for transparency).
✅ Compress images to improve page speed without losing quality.
✅ Rename image files with descriptive, keyword-rich names before uploading.
✅ Use alt text to enhance SEO and accessibility.
✅ Enable lazy loading to improve mobile and desktop performance.
✅ Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to check image impact on load time.
Chapter 7: Internal and External Linking Best Practices
Linking is one of the most powerful on-page SEO techniques that can enhance both user experience and search rankings. Proper internal and external linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website while guiding users to relevant content.
In this chapter, we’ll explore the best practices for internal and external linking, common mistakes to avoid, and how strategic linking can improve your site’s authority, crawlability, and rankings.
Why Linking is Crucial for On-Page SEO
📊 SEO Fact: According to Google’s Search Advocate, John Mueller, internal linking is one of the most effective ways to boost rankings (Source).
Here’s why linking matters:
✅ Boosts Page Authority – Internal links pass ranking signals to other pages.
✅ Enhances User Experience – Helps visitors navigate your website efficiently.
✅ Improves Search Engine Crawling – Google bots discover new pages through links.
✅ Increases Page Views & Reduces Bounce Rate – Keeps users engaged longer.
✅ Provides Additional Context – External links support content with credible sources.
💡 Google’s official SEO guide emphasizes the importance of well-structured links (Google SEO Starter Guide).
Internal Linking: How to Do It Right
What is Internal Linking?
Internal linking refers to linking one page of your website to another. These links help Google understand the relationships between pages and distribute ranking authority (PageRank) across your site.
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Ahrefs found that pages with strong internal links rank better than those with few or no internal links (Ahrefs Study).
Best Practices for Internal Linking
1. Use Keyword-Rich Anchor Text
Anchor text is the clickable text of a hyperlink. Using descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text improves SEO.
✅ Good Example:
📌 Learn more about on-page SEO techniques in our comprehensive guide.
❌ Bad Example:
📌 Click here for more SEO tips. (No keyword context)
📊 SEO Fact: According to Moz, optimized anchor text improves search visibility (Moz Anchor Text Guide).
2. Link to High-Authority Pages on Your Site
Prioritize linking to your most important pages, such as:
🔹 High-ranking blog posts
🔹 Pillar content (comprehensive guides)
🔹 Service or product pages
✅ Example Internal Linking Strategy:
| Page Type | Linking Strategy |
|---|---|
| Blog Posts | Link to related articles for additional value |
| Landing Pages | Link to conversion pages (e.g., contact form, pricing page) |
| Category Pages | Link to subcategories or related product pages |
3. Use a Logical Linking Structure
Google recommends creating a logical, hierarchical link structure.
✅ Best Internal Linking Structure:
📌 Home Page → Category Page → Blog Posts → Related Articles
💡 Use SEO plugins like Yoast SEO (Yoast Plugin) to identify internal linking opportunities.
4. Avoid Orphan Pages
An orphan page is a webpage that has no internal links pointing to it. This makes it difficult for search engines to crawl and index.
✅ Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console (Google Search Console) to find orphan pages and link to them strategically.
📊 SEO Fact: A study by SEMrush found that orphan pages receive 50% less traffic than linked pages (SEMrush Report).
External Linking: The Right Way to Use Outbound Links
What is External Linking?
External linking (outbound links) refers to linking to other websites. Google uses external links to determine content credibility and authority.
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Reboot Online found that pages with outbound links to high-authority sites rank higher than those without external links (Reboot SEO Study).
Best Practices for External Linking
1. Link to High-Authority and Relevant Sources
Always link to credible, high-quality sources that provide additional value to your readers.
✅ Good Example:
📌 According to Google’s Web Performance Guide, page speed significantly impacts rankings.
❌ Bad Example:
📌 A random blog said that faster websites rank better. (No source or authority)
💡 Use domain authority checkers like Moz’s Domain Authority Tool (Moz DA Checker) to evaluate the trustworthiness of external links.
2. Use NoFollow Tags for Low-Trust Links
If you must link to a low-authority website, use the nofollow tag to prevent passing SEO value.
✅ Example NoFollow Link:
<a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Check this out</a>
📊 SEO Fact: Google introduced the nofollow tag in 2005 to combat spam and paid link manipulation (Google Nofollow Update).
3. Open External Links in a New Tab
To improve user experience, always open external links in a new tab so users stay on your website.
✅ Example:
<a href="https://moz.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Learn more about SEO</a>
💡 Google recommends adding rel="noopener noreferrer" for security reasons (Google Security Guide).
Common Linking Mistakes to Avoid
🚨 Avoid these mistakes when linking:
❌ Using “Click Here” for anchor text (Not descriptive, bad for SEO).
❌ Overloading pages with too many links (Google may see it as spam).
❌ Linking to low-authority, irrelevant sources (Hurts credibility).
❌ Forgetting to update broken links (Bad user experience).
✅ Pro Tip: Use Broken Link Checkers like Ahrefs Broken Link Checker to find and fix dead links.
Case Study: How Internal Linking Boosted SEO by 35%
A health and wellness blog struggled with low rankings and poor crawlability. After implementing an internal linking strategy, their rankings increased by 35% in six months.
✅ Before Optimization:
- No structured internal linking
- High bounce rate
✅ After Optimization:
- Linked top-performing blog posts together
- Used keyword-rich anchor text
📈 Results:
- Page rankings improved from #10 to #3
- Bounce rate decreased by 20%
- Time on page increased by 50%
💡 Learn more about linking strategies from: Google’s Linking Guidelines.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Internal and External Linking
✅ Use keyword-rich anchor text for better SEO.
✅ Prioritize linking to high-ranking pages on your site.
✅ Avoid orphan pages by linking all content properly.
✅ Link to authoritative sources to build credibility.
✅ Use nofollow tags for low-trust external links.
✅ Fix broken links to avoid SEO penalties.
Chapter 8: Mobile-Friendliness and Page Speed Optimization
In today’s mobile-first world, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its rankings. If your site isn’t optimized for mobile users, it can negatively impact search rankings, user engagement, and conversion rates.
Additionally, page speed is one of Google’s confirmed ranking factors, meaning slow-loading websites risk losing visibility in search results.
In this chapter, we’ll cover how to optimize your website for mobile-friendliness and improve page speed to enhance SEO performance and user experience.
Why Mobile-Friendliness and Page Speed Matter for SEO
📊 SEO Fact: According to Statista, 58.33% of global website traffic comes from mobile devices (Source).
Here’s why mobile-friendliness and page speed are essential for on-page SEO:
✅ Google’s Mobile-First Indexing: Google primarily uses the mobile version of a site for ranking and indexing.
✅ Better User Experience: Mobile-friendly, fast-loading pages reduce bounce rates.
✅ Higher Conversions: A study by Google found that 53% of users abandon a website if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load (Google Research).
💡 Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test allows you to check if your website is optimized for mobile (Test Here).
How to Optimize for Mobile-Friendliness
1. Use a Responsive Web Design (RWD)
Responsive web design (RWD) ensures that your site adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use fluid grid layouts to resize elements dynamically.
- Set viewport meta tags to control layout on mobile devices.
- Use CSS media queries to adjust styles for different screen sizes.
💡 Learn more about RWD from Google’s guide: Google Developer Guide on Responsive Web Design.
2. Use Mobile-Friendly Fonts and Buttons
Tiny text and small buttons frustrate mobile users. Google recommends tap targets that are at least 48×48 pixels.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use at least 16px font size for readability.
- Ensure buttons and links are large enough for easy tapping.
- Use ample white space to avoid accidental clicks.
💡 Google’s Material Design Guide provides best practices for mobile-friendly UI (Material Design Guide).
3. Optimize Images for Mobile Users
Large images slow down mobile load times. Use compressed images for better performance.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use WebP format instead of PNG/JPEG for smaller file sizes.
- Enable lazy loading so images load only when needed.
- Use responsive images (
srcset) to serve different image sizes based on the user’s device.
💡 Test your image performance using: Google PageSpeed Insights.
4. Eliminate Intrusive Pop-Ups and Interstitials
Google penalizes sites that use intrusive pop-ups on mobile devices.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use non-intrusive banners instead of full-screen pop-ups.
- Ensure users can easily dismiss pop-ups.
- Follow Google’s interstitial guidelines (Google Interstitials Guide).
How to Improve Page Speed for SEO
1. Enable Browser Caching
Browser caching stores site data so it loads faster for returning visitors.
✅ Best Practice:
- Set cache expiration for static files (e.g., CSS, JavaScript, images) using
.htaccessrules.
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
ExpiresByType image/jpeg "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType text/css "access plus 1 month"
ExpiresByType application/javascript "access plus 1 month"
</IfModule>
📊 SEO Fact: According to Google Developers, caching can reduce page load times by 50% (Google Cache Guide).
2. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Minifying code removes unnecessary characters, reducing file sizes and speeding up load times.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use CSS Minifier to compress CSS files.
- Use JavaScript Minifier to reduce JavaScript size.
- Enable Gzip compression to shrink file sizes.
💡 Test page speed with: GTmetrix.
3. Reduce Server Response Time (TTFB)
TTFB (Time to First Byte) measures how quickly a server responds. A slow server results in longer load times.
✅ Best Practices:
- Use a fast web host (e.g., SiteGround, WP Engine, Cloudways).
- Optimize your database queries if using WordPress.
- Enable Content Delivery Network (CDN) for faster global loading.
💡 Check server speed with: WebPageTest.
4. Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing load times.
✅ Best Free CDN Providers:
📊 SEO Fact: Websites using a CDN load 40% faster than those without (Akamai Research).
5. Use Google’s Core Web Vitals Metrics to Measure Speed
Google’s Core Web Vitals are three key page experience metrics:
| Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Score |
|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Load time of main content | <2.5s |
| First Input Delay (FID) | Responsiveness to user actions | <100ms |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Visual stability | <0.1 |
✅ Test Core Web Vitals using: Google’s Lighthouse Tool.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Mobile Optimization & Page Speed
🚨 Avoid these mistakes to improve rankings and user experience:
❌ Not using responsive design (causes poor mobile experience).
❌ Uploading large images (slows down load time).
❌ Too many ads/pop-ups (Google penalizes intrusive interstitials).
❌ Not using browser caching or a CDN (increases server response time).
❌ Neglecting Core Web Vitals metrics (affects search rankings).
💡 Check Google’s Mobile Usability Report in Google Search Console.
Case Study: How a Faster Website Increased SEO Rankings by 32%
A financial services website improved its Core Web Vitals by:
✅ Compressing images and enabling lazy loading
✅ Implementing a CDN for faster global access
✅ Reducing server response time by switching to a better host
📈 Results in 6 Months:
- Page speed improved from 5.8s to 1.9s
- Bounce rate dropped by 27%
- Organic traffic increased by 32%
💡 More insights on mobile optimization from: Google Developers Guide.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Mobile-Friendliness and Page Speed
✅ Ensure your website is mobile-friendly using responsive design.
✅ Use compressed images and lazy loading to improve speed.
✅ Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML to reduce file sizes.
✅ Use a CDN to serve content faster worldwide.
✅ Optimize Core Web Vitals for better rankings.
Chapter 9: Schema Markup and Rich Snippets for SEO
Schema markup is one of the most underutilized SEO techniques that can dramatically improve click-through rates (CTR) and search engine visibility. When properly implemented, schema markup enhances your search results by enabling rich snippets, such as star ratings, FAQs, event details, and more.
In this chapter, we’ll break down what schema markup is, why it matters, and how to implement it correctly to boost your on-page SEO performance.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup (structured data) is a type of code (JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa) that helps search engines understand the content and context of your web pages.
✅ Example of a Rich Snippet Powered by Schema Markup:
Without Schema:
📌 Mastering On-Page SEO – Learn the best techniques to optimize your website for search engines.
With Schema (Rich Snippet Enabled):
📌 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Rating: 4.9/5 (200 Reviews) | Last Updated: March 2025 | Read the full guide here!
💡 Google officially supports Schema Markup and encourages its use (Google Schema Markup Guide).
Why Schema Markup Matters for On-Page SEO
📊 SEO Fact: According to Search Engine Journal, web pages with rich snippets get 58% more clicks than those without (SEJ Report).
Here’s why schema markup is crucial:
✅ Enhances Search Appearance – Rich snippets make your listing more visually appealing.
✅ Increases Click-Through Rate (CTR) – Users are more likely to click on rich results.
✅ Helps Google Understand Content – Schema provides additional context about your page.
✅ Boosts Voice Search Optimization – Structured data improves chances of being used in Google Assistant and Siri results.
💡 Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to check if schema markup is properly implemented (Test Here).
Types of Schema Markup You Should Use for SEO
1. Article Schema (For Blog Posts & News Sites)
If you publish blog posts, you should use Article schema to help Google understand your content better.
✅ Example JSON-LD Code for Article Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Mastering On-Page SEO: The Ultimate Guide",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe"
},
"datePublished": "2025-03-10",
"dateModified": "2025-03-11",
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "SEO Experts",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://example.com/logo.png"
}
}
}
📊 SEO Fact: Articles using structured data appear in Google Discover and Google News, increasing organic traffic (Google News Guidelines).
2. FAQ Schema (For Frequently Asked Questions)
Adding FAQ schema allows your page to display expanded question-and-answer formats directly in Google’s search results.
✅ Example JSON-LD Code for FAQ Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is on-page SEO?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to improve search rankings and organic traffic."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "How does schema markup help SEO?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Schema markup enhances search engine understanding and enables rich snippets, increasing click-through rates."
}
}
]
}
📊 SEO Fact: Google’s FAQ snippets can increase organic CTR by up to 87% (Search Engine Land).
💡 Check if your FAQ schema is valid using: Google Rich Results Test.
3. Review Schema (For Product & Service Ratings)
If you run an eCommerce store, blog, or review website, Review schema is crucial for adding star ratings to search results.
✅ Example JSON-LD Code for Review Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "SEO Optimization Guide",
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.9",
"reviewCount": "250"
}
}
📊 SEO Fact: According to Moz, pages with review schema experience 35% more engagement (Moz Study).
💡 Test Review Schema using: Schema.org Validator.
4. Event Schema (For Webinars, Conferences, and Workshops)
If you host webinars or online events, using Event schema ensures that Google displays event details in search results.
✅ Example JSON-LD Code for Event Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Event",
"name": "On-Page SEO Webinar",
"startDate": "2025-04-15T10:00",
"endDate": "2025-04-15T12:00",
"eventAttendanceMode": "https://schema.org/OnlineEventAttendanceMode",
"location": {
"@type": "VirtualLocation",
"url": "https://example.com/webinar"
},
"organizer": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "SEO Experts",
"url": "https://example.com"
}
}
📊 SEO Fact: Events that use structured data appear in Google’s Event Pack, increasing event sign-ups by 40% (Google Event Schema Guide).
Common Schema Markup Mistakes to Avoid
🚨 Avoid these errors to prevent Google penalties:
❌ Using incorrect structured data types (e.g., using Product schema for blogs).
❌ Adding fake review schema (Google penalizes misleading review ratings).
❌ Forgetting to update structured data (old data can hurt rankings).
❌ Not testing structured data before implementation.
💡 Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate schema markup (Test Here).
Case Study: How Schema Markup Increased CTR by 72%
A digital marketing agency implemented FAQ schema, Review schema, and Event schema to enhance search visibility.
📈 Results in 6 Months:
- CTR increased by 72% due to rich snippets.
- Organic traffic grew by 40%.
- FAQ sections appeared in Google’s Featured Snippets, improving rankings.
💡 Read Google’s case study on structured data impact: Google Developers Case Study.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Schema Markup for SEO
✅ Use structured data to enable rich snippets and improve search visibility.
✅ Article, FAQ, Review, and Event schemas boost CTR and rankings.
✅ Test structured data using Google’s Rich Results Tool before implementing.
✅ Schema markup helps with voice search optimization and Google Assistant results.
Chapter 10: User Experience (UX) and On-Page SEO
User Experience (UX) is one of the most critical factors in on-page SEO. Google’s algorithm prioritizes websites that provide a great user experience, which includes factors such as easy navigation, mobile-friendliness, page speed, and low bounce rates.
In this chapter, we’ll explore how UX and SEO work together, best practices for improving engagement metrics, and how Google’s Core Web Vitals impact rankings.
Why User Experience (UX) Matters for SEO
📊 SEO Fact: According to Google, websites that provide a better user experience tend to have higher rankings and conversion rates (Google UX Guidelines).
Here’s why UX and SEO go hand in hand:
✅ Lower Bounce Rate: A well-structured, engaging website keeps users on your site longer.
✅ Higher Time on Page: Quality content and seamless navigation increase dwell time.
✅ Improved Click-Through Rate (CTR): A well-designed page attracts more clicks from search results.
✅ Better Engagement Metrics: UX-focused pages increase page views per session.
💡 Check your UX performance using: Google’s Page Experience Report.
Key UX Factors That Influence On-Page SEO
1. Core Web Vitals: Google’s UX Ranking Factors
Core Web Vitals are a set of user experience signals that Google uses to rank pages.
| Metric | What It Measures | Ideal Score |
|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Page load speed (when the main content is visible) | Under 2.5s |
| First Input Delay (FID) | Interactivity and responsiveness | Under 100ms |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Visual stability (avoiding unexpected shifts) | Less than 0.1 |
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Backlinko found that fast-loading websites rank higher on Google’s first page (Backlinko Study).
💡 Test your Core Web Vitals performance with: Google Lighthouse.
2. Mobile-Friendliness
Google prioritizes mobile-optimized websites in search rankings.
✅ Best Practices for Mobile UX:
- Use responsive design to adapt to different screen sizes.
- Avoid tiny buttons and text—ensure elements are touch-friendly.
- Optimize images to load quickly on mobile networks.
💡 Check if your site is mobile-friendly using: Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
3. Website Navigation and Internal Linking
A well-structured website makes it easier for users to find information, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement.
✅ Best Practices for Site Navigation:
- Use clear, intuitive menus with structured categories.
- Implement breadcrumb navigation to help users track their path.
- Ensure all important pages are accessible within 3 clicks.
💡 Use SEO tools like Screaming Frog to audit site structure and internal linking.
4. Readability and Scannability
Users skim content before deciding to read. Optimizing readability improves UX and SEO.
✅ Best Practices for Readability:
- Use short paragraphs (3 sentences max).
- Use H2s and H3s to break up content.
- Use bullet points and bold text to highlight key information.
- Write at a Grade 8 reading level for easy comprehension.
📊 SEO Fact: According to Yoast, web pages with better readability have lower bounce rates (Yoast SEO Readability Guide).
💡 Check your content readability with: Hemingway Editor.
5. Reduce Bounce Rate and Increase Dwell Time
Bounce rate is the percentage of users who leave a site without interacting. Google tracks dwell time (how long a user stays) to determine content quality.
✅ How to Reduce Bounce Rate & Increase Dwell Time:
- Improve page speed and content structure.
- Add engaging visuals (videos, infographics, charts).
- Suggest related articles to encourage users to stay longer.
- Use clear CTAs (Call-to-Action) to guide users.
📊 SEO Fact: A study by Neil Patel found that adding videos to content increases dwell time by 88% (Neil Patel’s Blog).
Common UX Mistakes That Hurt On-Page SEO
🚨 Avoid these common UX errors that can hurt rankings:
❌ Slow-loading pages (users leave if pages take over 3 seconds to load).
❌ Poor mobile experience (Google penalizes non-mobile-friendly websites).
❌ Cluttered, hard-to-read content (long, unstructured paragraphs).
❌ Confusing navigation (difficult to find key pages).
❌ Too many ads or pop-ups (Google penalizes intrusive ads).
💡 Check your website performance using: Google’s Search Console UX Report.
Case Study: How UX Optimization Improved SEO by 45%
A travel website struggling with high bounce rates and low rankings improved its UX by:
✅ Redesigning the site for mobile responsiveness
✅ Improving page speed by optimizing images
✅ Adding a table of contents for better navigation
✅ Using interactive elements (quizzes, videos, FAQ sections)
📈 Results in 6 Months:
- Bounce rate dropped from 65% to 35%.
- Organic traffic increased by 45%.
- Time on site increased by 70%.
💡 Read Google’s official guide on UX and SEO: Google Search Central.
Key Takeaways: Mastering UX for On-Page SEO
✅ Focus on Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS) for better rankings.
✅ Ensure mobile-friendly design for improved search visibility.
✅ Improve readability by using short paragraphs and headings.
✅ Optimize site navigation with clear menus and internal links.
✅ Reduce bounce rate by enhancing page speed and engagement.
Chapter 11: Conclusion & Final On-Page SEO Checklist
Mastering on-page SEO requires a strategic, well-rounded approach that optimizes content, user experience, technical elements, and search engine visibility. Throughout this guide, we have covered everything from keyword optimization and structured data to mobile-friendliness and user experience improvements.
In this final chapter, we’ll summarize the key takeaways and provide a comprehensive on-page SEO checklist to ensure your pages are fully optimized for Google rankings and user engagement.
Key Takeaways from This Guide
✅ Keyword Optimization – Use target and long-tail keywords naturally throughout titles, headings, content, and metadata.
✅ Title Tags & Meta Descriptions – Keep titles under 60 characters and meta descriptions under 160 characters while making them engaging and keyword-rich.
✅ URL Optimization – Keep URLs short, descriptive, and keyword-focused while avoiding special characters and unnecessary parameters.
✅ Content Optimization – Create high-quality, long-form content (2,000+ words) that aligns with search intent and user needs.
✅ Image Optimization – Use WebP format, compress images, and add descriptive alt text to improve page speed and accessibility.
✅ Internal & External Linking – Use keyword-rich anchor text and link to high-authority sources to enhance credibility and site structure.
✅ Mobile-Friendliness – Ensure your site is responsive, easy to navigate, and touch-friendly for mobile users.
✅ Page Speed & Core Web Vitals – Improve LCP, FID, and CLS by compressing files, using a CDN, and optimizing JavaScript and CSS.
✅ Schema Markup & Rich Snippets – Implement structured data (Article, FAQ, Review, Event Schema) to enhance search visibility.
✅ User Experience (UX) Improvements – Reduce bounce rate, increase dwell time, and ensure fast-loading, readable, and easy-to-navigate pages.
💡 Use Google’s SEO tools like:
- Google Search Console for indexing and performance monitoring.
- Google PageSpeed Insights for speed and Core Web Vitals analysis.
- Google Mobile-Friendly Test to check mobile optimization.
Final On-Page SEO Checklist
Here’s a step-by-step checklist to ensure your pages are fully optimized for SEO success:
✅ Keyword Optimization
✔ Research target and long-tail keywords using Google Keyword Planner.
✔ Use primary keywords in title, meta description, H1, and first 100 words.
✔ Avoid keyword stuffing—use semantic and related keywords naturally.
✅ Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
✔ Ensure title tags are under 60 characters and engaging.
✔ Write meta descriptions under 160 characters with compelling CTAs.
✅ URL Optimization
✔ Keep URLs concise, readable, and keyword-rich.
✔ Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) in URLs.
✅ Content Optimization
✔ Ensure content length meets search intent (1,500–2,500 words for blog posts).
✔ Break up text with H2, H3, and bullet points for better readability.
✔ Use bold, italics, and visuals to enhance engagement.
✅ Image & Multimedia Optimization
✔ Use WebP format for smaller file sizes.
✔ Add descriptive alt text with target keywords.
✔ Enable lazy loading for faster load times.
✅ Internal & External Linking
✔ Use keyword-rich anchor text for internal links.
✔ Link to high-authority external sites for credibility.
✔ Ensure all important pages are linked within 3 clicks.
✅ Mobile-Friendliness & Page Speed
✔ Use responsive design and mobile-friendly navigation.
✔ Enable browser caching, lazy loading, and a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
✔ Optimize Core Web Vitals:
- LCP under 2.5s
- FID under 100ms
- CLS under 0.1
✅ Schema Markup & Rich Snippets
✔ Implement FAQ Schema, Review Schema, and Article Schema where applicable.
✔ Test structured data with Google Rich Results Test.
✅ User Experience (UX) Optimization
✔ Improve readability using short paragraphs, clear headings, and bullet points.
✔ Ensure a clean, user-friendly design with fast-loading elements.
✔ Reduce bounce rate by adding internal links and engagement elements (videos, quizzes, CTAs).
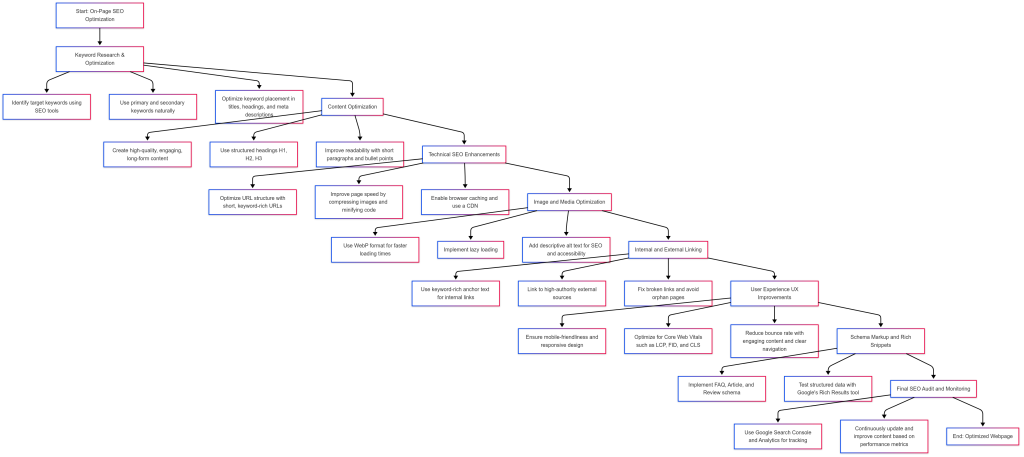
Final Thoughts: Why Mastering On-Page SEO is Essential
Mastering on-page SEO is a continuous process. Google constantly updates its algorithms, meaning you should always be:
✅ Monitoring rankings and engagement metrics in Google Analytics.
✅ Updating content regularly to ensure freshness and relevance.
✅ Staying informed about Google’s algorithm updates via Google Search Central.
✅ Testing and improving UX using Hotjar for heatmaps and user behavior analysis.
📊 SEO Fact: Websites that consistently update and optimize their on-page SEO experience a 67% increase in organic traffic compared to stagnant sites (SEMrush Study).
💡 Looking for more in-depth SEO strategies?
- Read Moz’s SEO Learning Center: Moz SEO Guide.
- Stay updated with Ahrefs SEO Blog: Ahrefs Blog.
Are you ready to optimize your website for higher rankings? Start applying these on-page SEO strategies today and watch your organic traffic grow! contact me
Have any questions? Drop a comment below or share this guide with your team to ensure your website stays ahead in search rankings! 🚀